Study Shows Contact with CPS Too High and Disproportionate by Race and Ethnicity
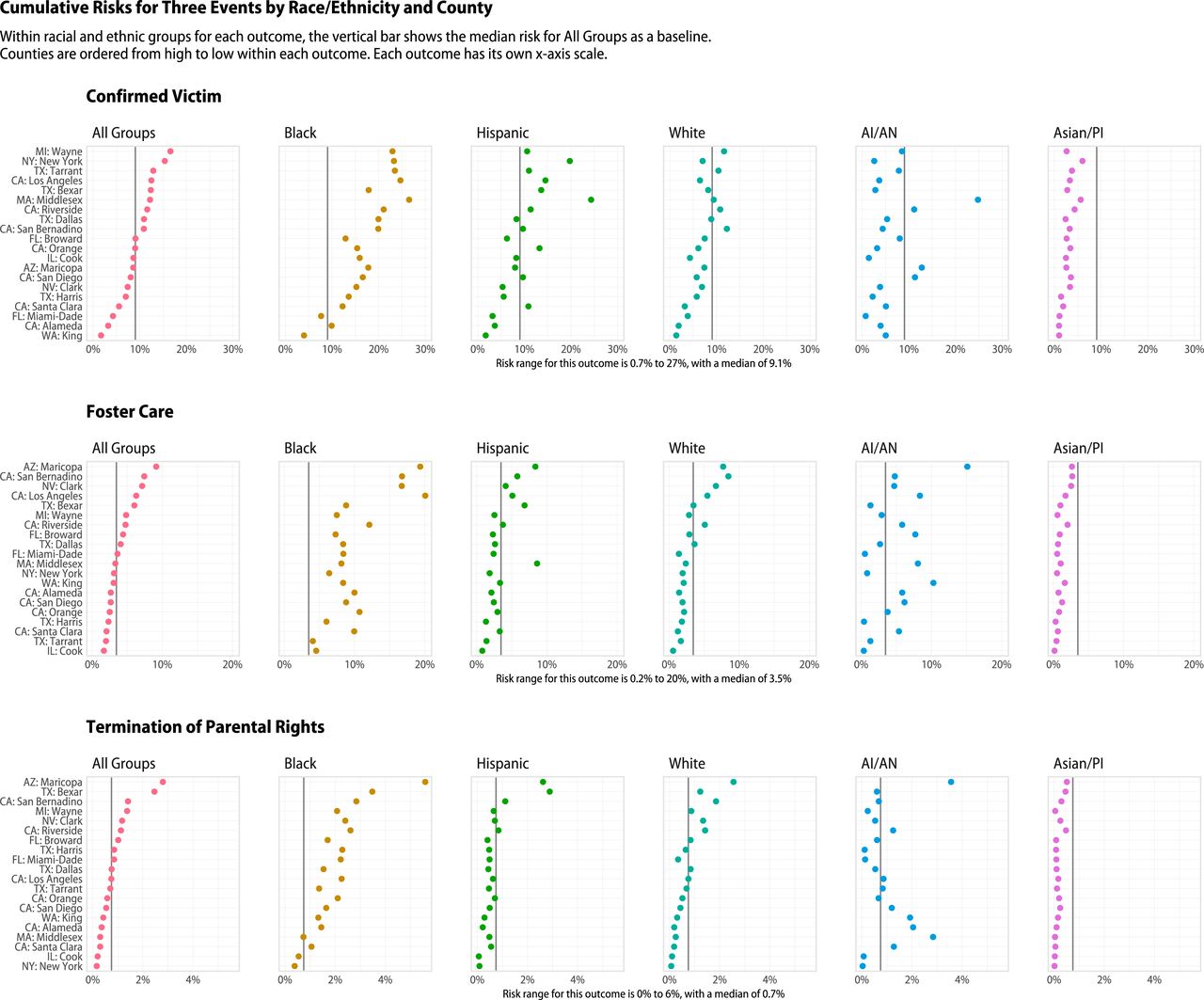
A recent report from the Proceedings of the National Academy of the Sciences found that for many children in the United States, especially Black children, encounters with the child welfare system are commonplace. The study looked at the prevalence of contact with Child Protective Services (CPS) across the 20 most populous counties in the U.S., including Maricopa County. The peer-reviewed study found that contact with Child Protective Services is much more common than previously thought.
- 1 in 3 children will ever have a CPS investigation,
- 1 in 8 will ever experience confirmed maltreatment
- 1 in 17 will ever be placed in foster care, and
- 1 in 100 will ever have parental rights terminated
The study also found that the risk of CPS contact was unequally distributed by race and ethnicity. Black children had consistently higher rates of investigations. Including Maricopa County, Black children had risks of investigation that exceeded 60%. Black children also experienced very high rates of later-stage involvement in nearly all counties. Rates routinely exceeded 20% for confirmed maltreatment, 10% for foster care placement, and 2% for termination of parental rights. Maricopa County was cited as having comparatively extreme rates of foster care placement and termination of parental rights for all children, leading to very high rates of both events for all racial and ethnic groups except Asian/Pacific Islanders. The county had the second-highest risk rate for placement in foster care and the highest risk for terminating the parental rights of Black children.
Learn more about racial and ethnic disproportionality in Arizona’s child welfare system.